BMW 3: Overview
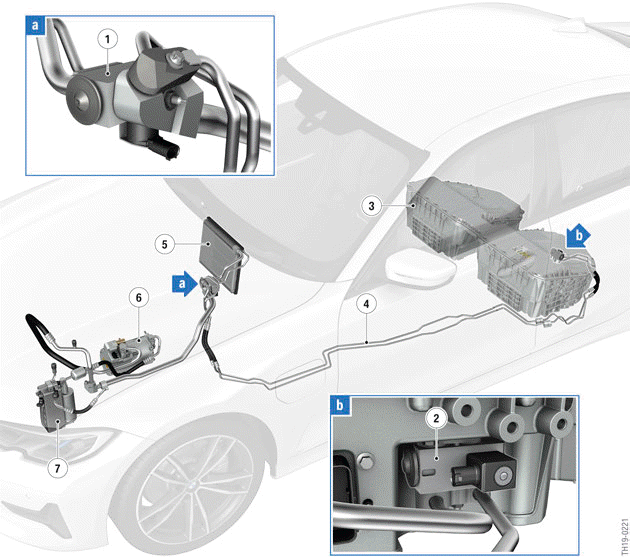
G20 PHEV, system overview of climate control - Installation locations
- Combined expansion and shutoff valve at the evaporator
- Combined expansion and shutoff valve at the high-voltage battery unit
- High-voltage battery unit
- Refrigerant lines to high-voltage battery unit
- Evaporator, passenger compartment
- Electric A/C compressor (EKK)
- Coolant-based air conditioning condenser (coolant-refrigerant-heat exchanger)
Cooling system of the high-voltage battery unit
The high-voltage battery unit is cooled directly using R1234yf . The refrigerant circuit of the air conditioning consists of 2 parallel branches. One for cooling the passenger compartment and one for cooling the high-voltage battery unit. For each branch there is a combined expansion and shutoff valve in order to be able to control the cooling functions independent of each other. The battery management electronics can activate and open the combined expansion and shutoff valve at the high- voltage battery unit by applying voltage. In this way refrigerant can flow to the high-voltage battery unit. The cooling of the passenger compartment is also effected in a condition-based manner. The combined expansion and shutoff valve upstream from the evaporator can also be activated electrically by the EME. The amount of flowing refrigerant is adjusted thermally (depending on the refrigerant temperature) via the expansion valves.
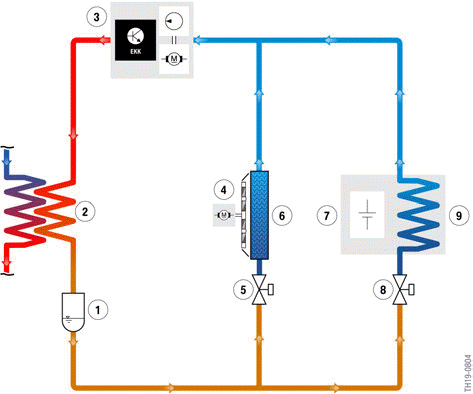
Refrigerant circuit with high-voltage battery unit (simplified illustration)
- Receiver dryer
- Coolant-based air conditioning condenser (coolant-refrigerant-heat exchanger)
- Electric A/C compressor (EKK)
- Blower for passenger compartment
- Combined expansion and shutoff valve, passenger compartment
- Evaporator, passenger compartment
- High-voltage battery unit
- Combined expansion and shutoff valve, high-voltage battery unit
- Heat exchanger
As a result of the pressure drop after the expansion valve, the refrigerant in the lines and coolant ducts of the high-voltage battery unit evaporates. In the process the refrigerant absorbs heat energy from the cell modules or battery cells and cools them. The evaporated refrigerant then leaves the high-voltage battery unit, is compressed by the electric A/C compressor and liquefied in the coolant/refrigerant heat exchanger. Although energy is required from the high-voltage electrical system for this procedure, it is of utmost importance. Only this way can a long service life and a high degree of efficiency of the battery cells be guaranteed.

